<meta>
Metadata refers to information about a webpage that isn’t directly visible to users but helps browsers, search engines, and social networks understand and display the page correctly. These small pieces of data, usually added inside the <head> of an HTML document, influence how your page behaves, appears in search results, and is shared on social media. Well-implemented metadata improves SEO, accessibility, and user experience across devices and platforms.
Viewport
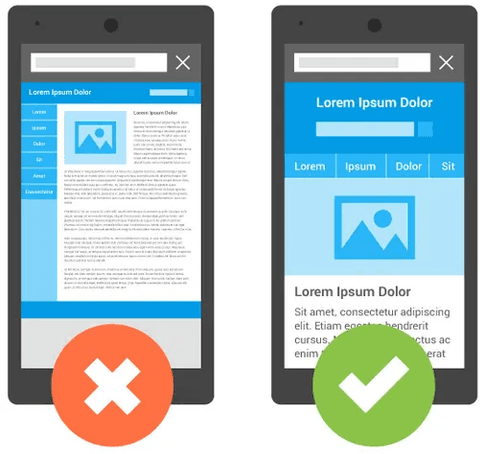
Viewport Tag: This meta tag is crucial for responsive design. It sets the width of the viewport to the device width and controls the initial scale of the page. This ensures that the layout is optimized for mobile devices, making the content easily readable without requiring zooming
<meta
name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"
>
Description
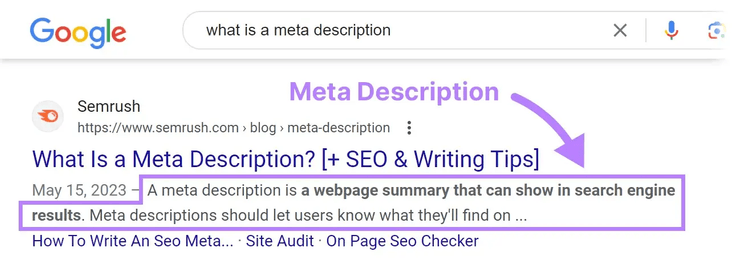
Description Tag: This tag provides a brief description of the page content. It's often used by search engines to display a summary in search results. A well-crafted description can improve click-through rates from search results, as it gives users a clear idea of what the page is about before they click
<meta
name="description"
content="Learn how to use meta tags effectively"
>
Robots
Robots Tag: This controls how search engine crawlers interact with your page. You can instruct search engines to index your page or not, and whether to follow links. his is useful for pages that you do not want to appear in search results or for controlling the flow of search engine crawling on your site
<meta name="robots" content="index, follow">
<meta name="robots" content="noindex, nofollow">
Name Attribute:
The “name” attribute indicates which crawler the instructions apply to. To address all crawlers, set name="robots". To target specific search engines, use their crawler names (e.g., Googlebot, Bingbot)
Content Attribute:
The “content” attribute contains instructions for the crawler:
-
Noindex => Tells crawlers not to index or display the page in search results. Commonly used for cart or checkout pages.
-
Nofollow => Tells crawlers not to follow any links on the page. The nofollow attribute is useful if you don’t control the links on a page, such as in user-generated content.
Open Graph
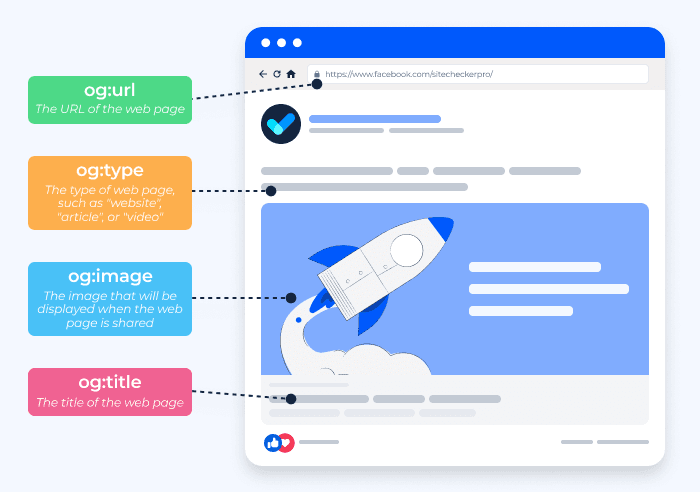
Open Graph Tags: These are essential for defining how URLs are displayed when shared on social media platforms like Facebook and Twitter. They allow you to specify the title, description, image, and more. These tags help ensure that when your content is shared, it carries with it a visually appealing preview and accurate description, potentially increasing engagement rates
<meta
property="og:title"
content="Introduction to Meta Tags"
>
<meta
property="og:description"
content="A comprehensive guide to using HTML"
>
<meta
property="og:image"
content="http://example.com/thumbnail.jpg"
>
<meta
property="og:url"
content="http://example.com/page.html"
>