2 - Object Storage + CDN
A very popular way to deploy an SPA is to use object storage for files and place a Content Delivery Network (CDN) in front for global performance. This strategy is cost-effective, highly scalable, and widely used in production environments.
Examples in Major Cloud Providers
This architecture is a standard pattern offered by all major cloud providers. While the service names differ, the core concept remains the same: a durable storage backend with a fast, global caching layer in front.
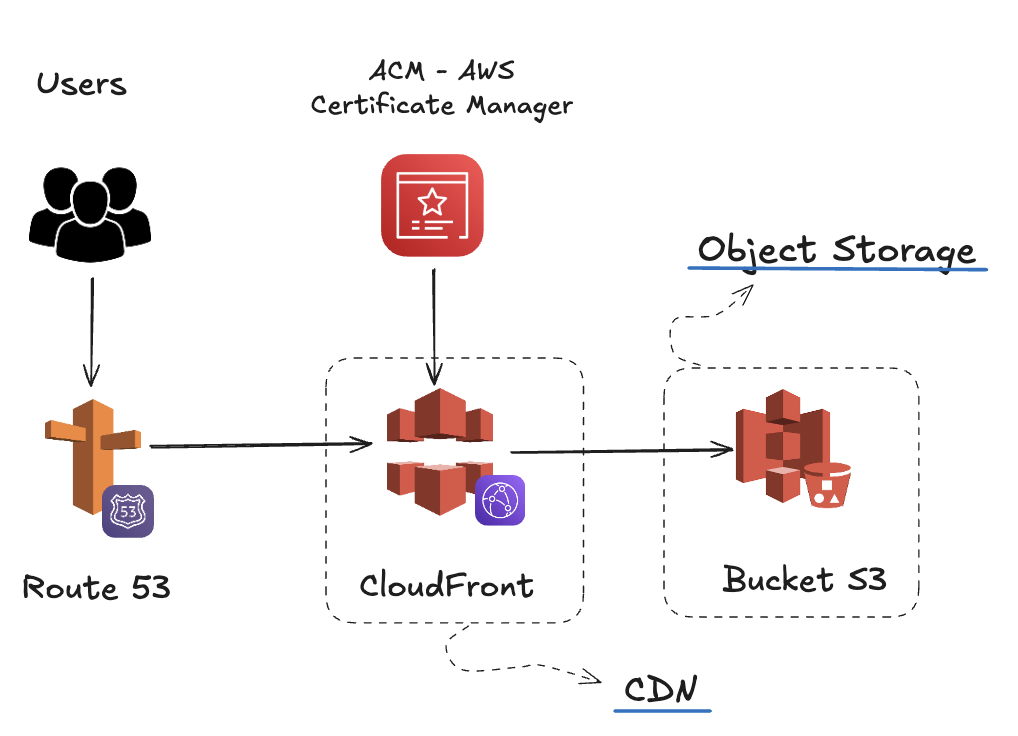
AWS: S3 + CloudFront: On Amazon Web Services (AWS), the go-to combination is Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) for object storage and Amazon CloudFront for the CDN.
- Amazon S3: You create an S3 "bucket" and upload your application's static build files (index.html, JavaScript bundles, CSS, and assets). It's designed for extreme durability and low-cost storage.
- Amazon CloudFront: You configure a CloudFront "distribution" to use the S3 bucket as its origin. CloudFront caches your files at edge locations around the world, drastically reducing latency for your users. It also handles routing fallbacks for SPAs and integrates seamlessly with AWS Certificate Manager (ACM) for free SSL/TLS certificat.
Google Cloud: Cloud Storage + Cloud CDN: On Google Cloud Platform (GCP), this pattern is implemented using Google Cloud Storage and Cloud CDN.
- Google Cloud Storage: Similar to S3, you create a "bucket" to store your static files.
- Cloud CDN: This service leverages Google's premium global network to deliver content quickly. The typical setup involves configuring an external HTTPS Load Balancer, which uses your Cloud Storage bucket as a "backend". This combination gives you fine-grained control over caching and routing rules, including the necessary rewrites for SPA client-side routing.
Microsoft Azure: Blob Storage + Azure CDN: On Microsoft Azure, the solution involves Azure Blob Storage and Azure CDN.
- Azure Blob Storage: You use a storage account and enable its "static website" hosting feature. This creates a special container ($web) where you upload your build artifacts.
- Azure CDN: You create a CDN profile and an "endpoint" that points to the static website URL provided by Blob Storage. Azure CDN then caches the content globally. Its rules engine can be configured to handle the URL rewrites required for deep links in an SPA to function correctly.
Platform Highlights
Cheap and durable storage
Object storage services (like Amazon S3) provide near-infinite, reliable storage at very low cost. Your build files (index.html, JS, CSS, assets) are uploaded directly to a bucket.
Global CDN distribution
A CDN caches your files on edge servers worldwide. Users are routed to the nearest server, reducing latency and improving loading times.
HTTPS with managed certificates
Attach a TLS certificate (e.g., AWS ACM) to the CDN distribution so your app is always served securely.
SPA fallback for client-side routing
The CDN is configured to rewrite unknown routes to index.html, ensuring deep links (/dashboard, /settings) load correctly.
Scales automatically
Because it’s built on storage + CDN, it scales seamlessly to millions of requests without managing servers.
Typical Workflow
- Build your SPA →
npm run build→ output (dist/orbuild/). - Upload files to a storage bucket (e.g., S3).
- Configure CDN with the bucket as origin:
- Cache assets aggressively.
- Short TTL for
index.html. - Enable SPA fallback (rewrite 404 →
/index.html).
- Enable HTTPS with a managed cert.
- Update DNS to point your custom domain (
example.com) to the CDN. - Invalidate cache for
index.htmlon every new deploy.
✅ Pros
- Very cheap at scale.
- Highly reliable and globally distributed.
- Fine control over caching and headers.
- No server management required.
❌ Cons
- More setup effort than PaaS.
- Must handle CDN invalidations for new deploys.
- Multiple components (bucket, CDN, cert) to configure.
🎯 When to Use
- You expect high traffic and need a cost-efficient solution.
- Your team is comfortable with cloud infrastructure.
- You want flexibility and scalability without vendor lock-in to PaaS platforms.