Scale From Zero To Millions
Step 1 - A single server
-
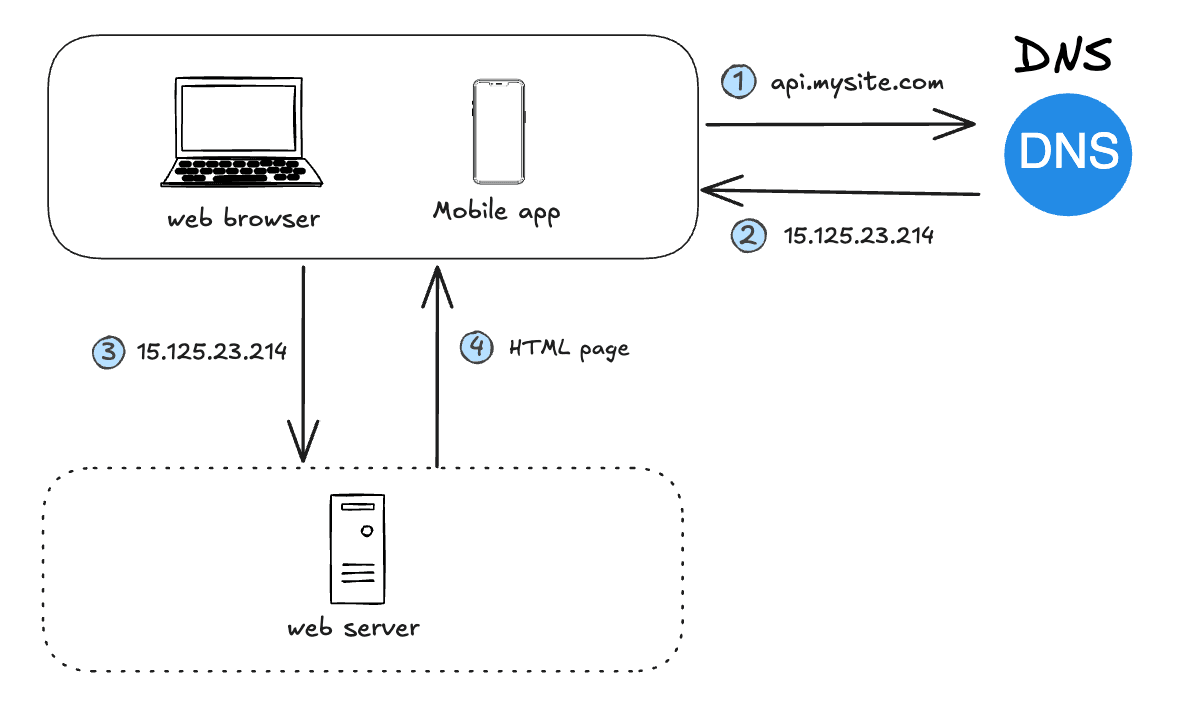
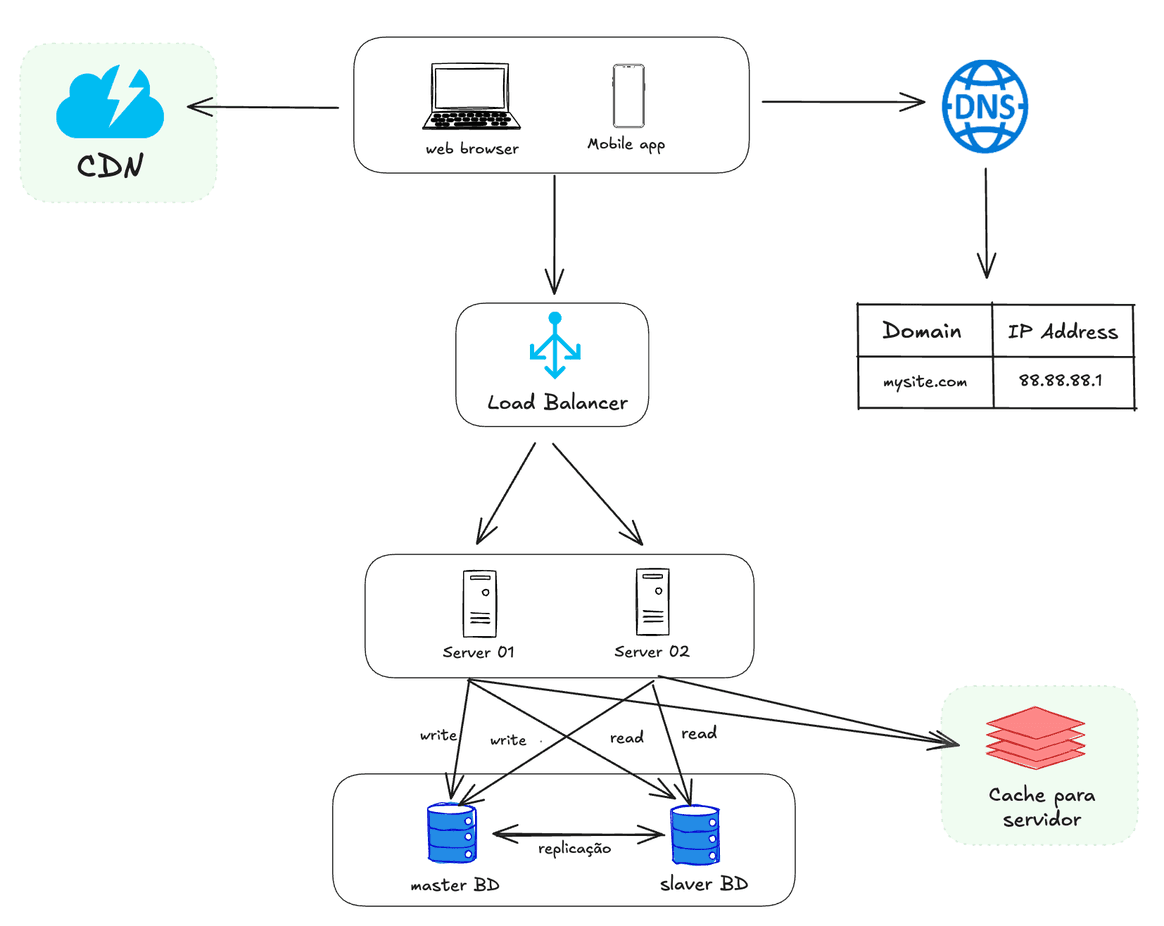
Users access websites through domain names, such as api.mysite.com. Typically, the Domain Name System (DNS) is a paid service provided by a third party and not hosted on our servers.
-
The Internet Protocol (IP) address is returned to the browser or mobile application. In the example, the IP address 15.125.23.214 is returned.
-
Once the IP address is obtained, Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) requests are sent directly to your web server.
-
The web server returns HTML pages or JSON responses for rendering
Step 2 - Adding a Database
-
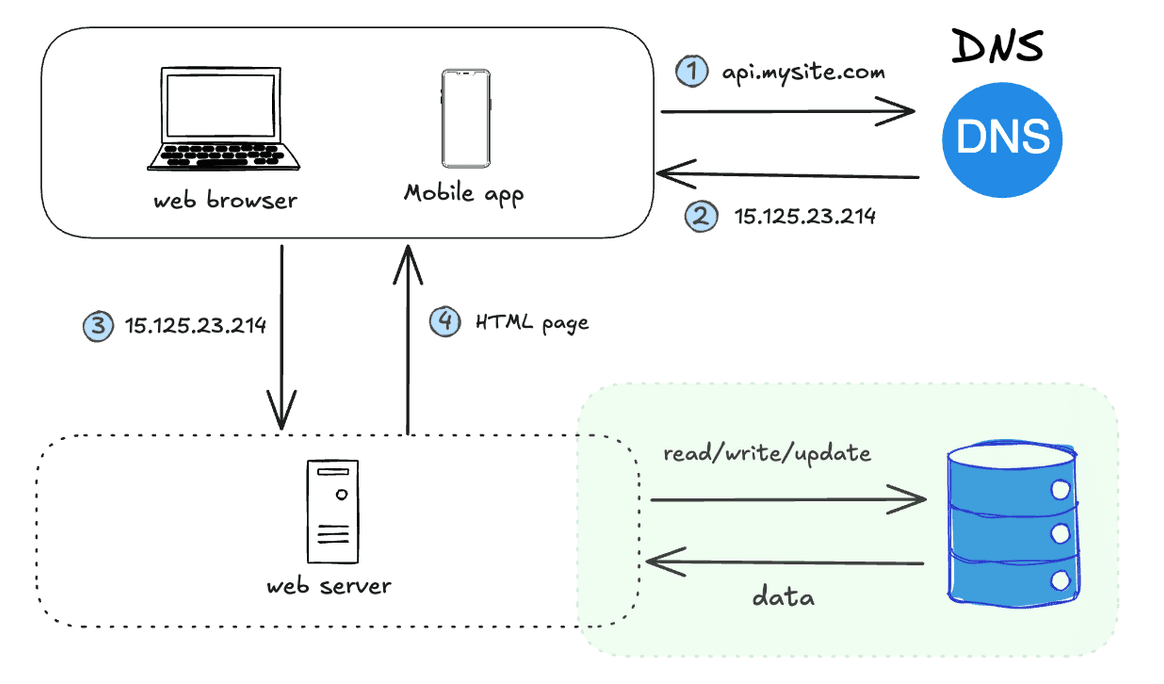
As the user base grows, one server is not enough, and we need multiple servers: one for web/mobile traffic, another for database.
-
Separar o tráfego web/móvel (camada web) e os servidores de banco de dados (camada de dados) permite que eles sejam dimensionados de forma independente.
Step 3 - Load Balancer
-
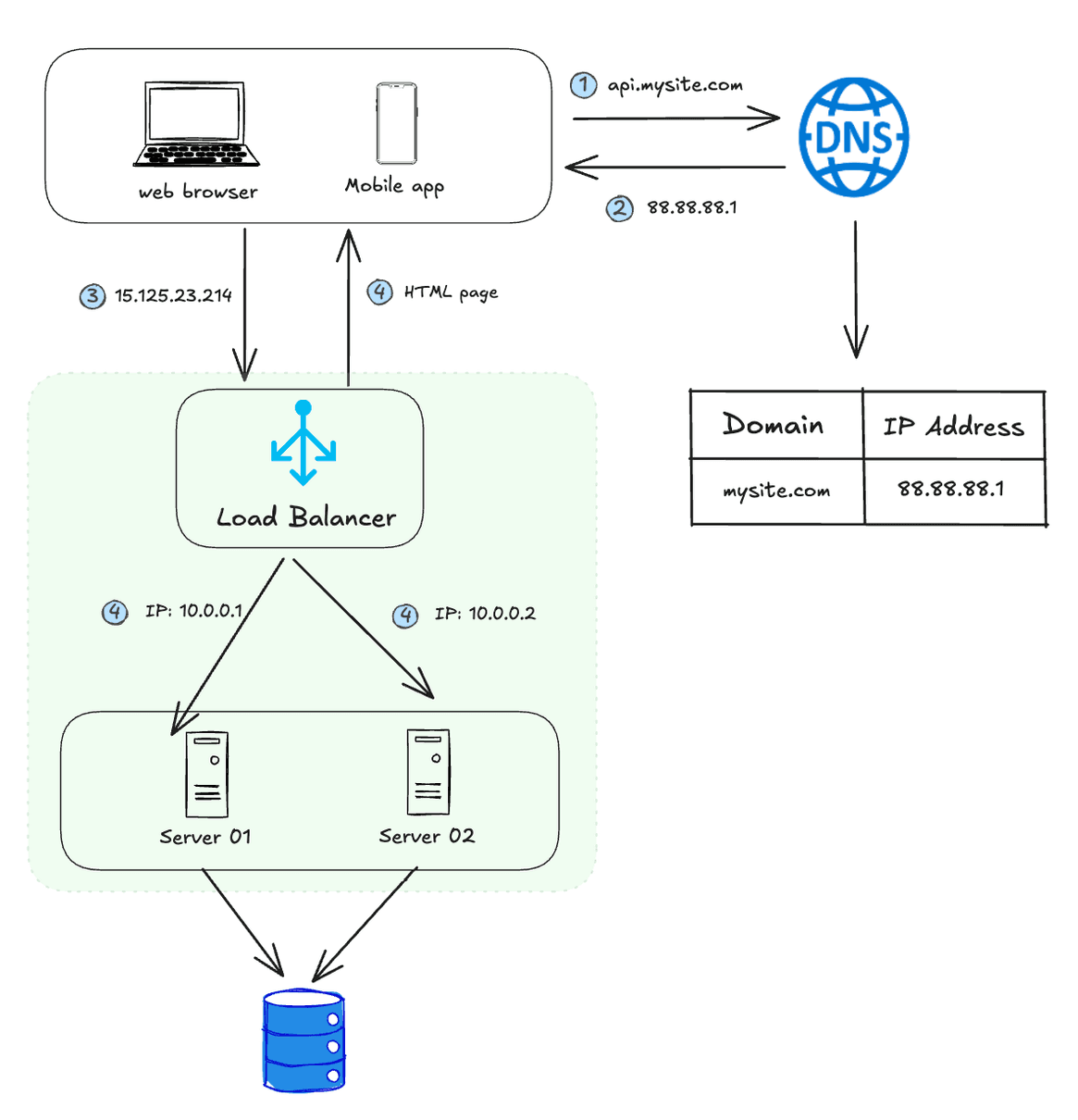
A load balancer distributes network requests or traffic efficiently across multiple servers in a system.
-
Its primary function is to improve responsiveness and service availability by preventing overloading of any individual server, thus ensuring that performance is optimized and that the user experience is consistent and reliable.
Step 4 - Database Replication
-
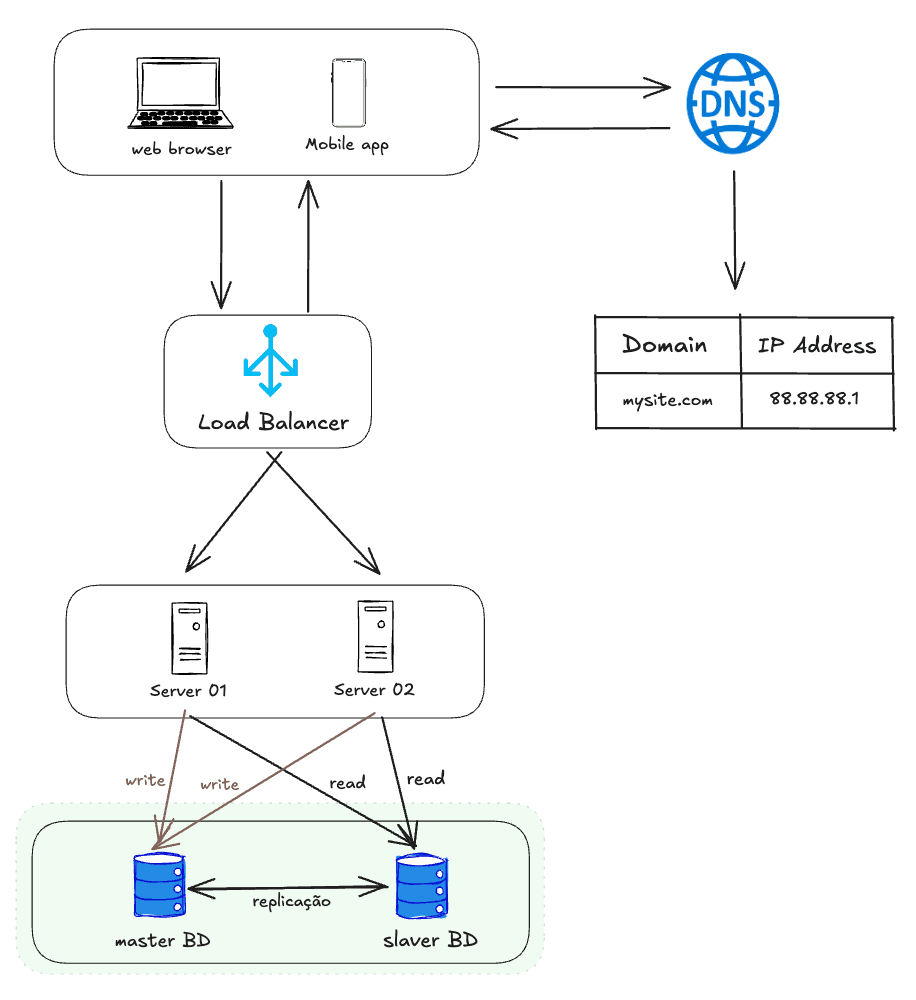
The master-slave database replication strategy involves a primary server (master) that processes and manages all writes and updates, while one or more secondary servers (slaves) synchronize these changes from the master and handle reads.
-
This approach relieves the burden on the primary server, distributes read queries among the secondary servers, and increases data availability and resilience.
Step 5 - Cache
Caching is a technique used to temporarily store data in quickly accessible locations to reduce the time it takes to retrieve that data for future requests.
5.1 - CDN - Content Delivery Network
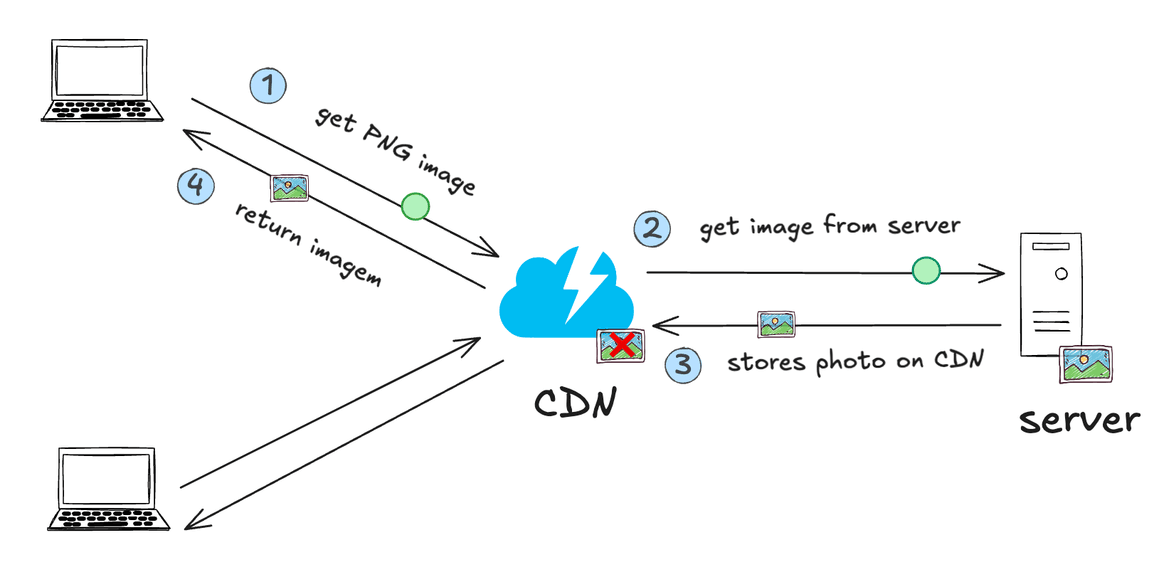
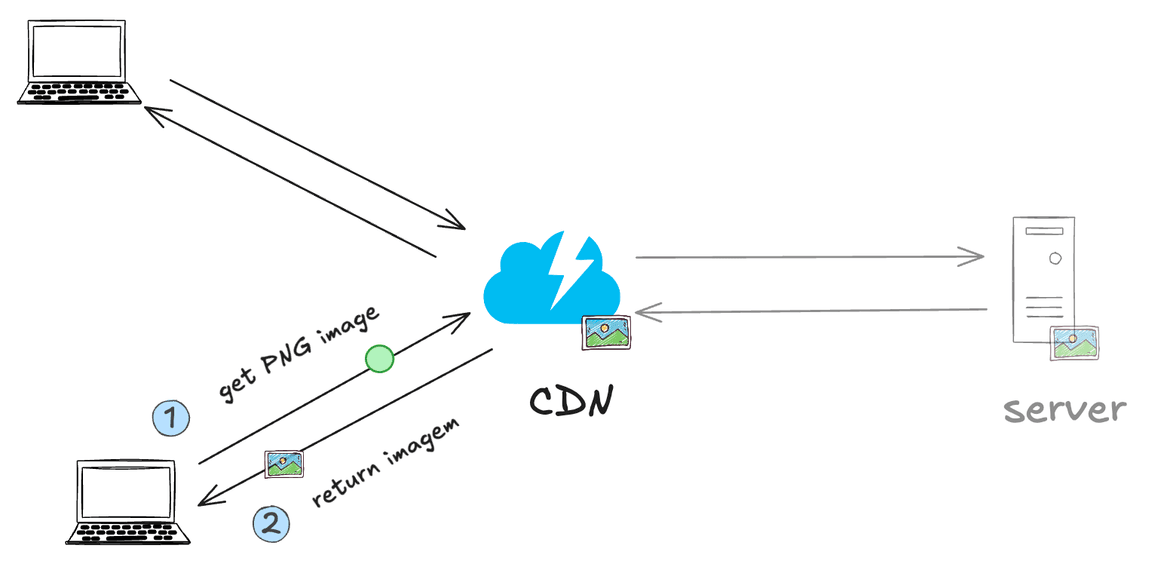
- A CDN (Content Delivery Network) uses the concept of caching to store copies of static content, such as images, videos, CSS and JavaScript files, on multiple geographically distributed proxy servers. When a user requests a file, the CDN redirects that request to the server that is geographically closest to the user, where a copy of the file is cached. This minimizes latency, reduces traffic at the origin (main server) and improves the loading speed of resources, providing a faster and more reliable user experience.
5.2 - Server-Side Caching to Avoid Database Queries
- Caching can be implemented to store data that is frequently queried, such as results from database queries or intensive computations. For example, product information on an e-commerce site or search results can be cached on the server. When a user requests this information, the server first checks to see if an up-to-date copy already exists in the cache
5.3 - Resume
-
Static assets (JS, CSS, images, etc.) are no longer served by web servers. They are fetched from CDN for better performance.
-
Database load is alleviated by caching data.
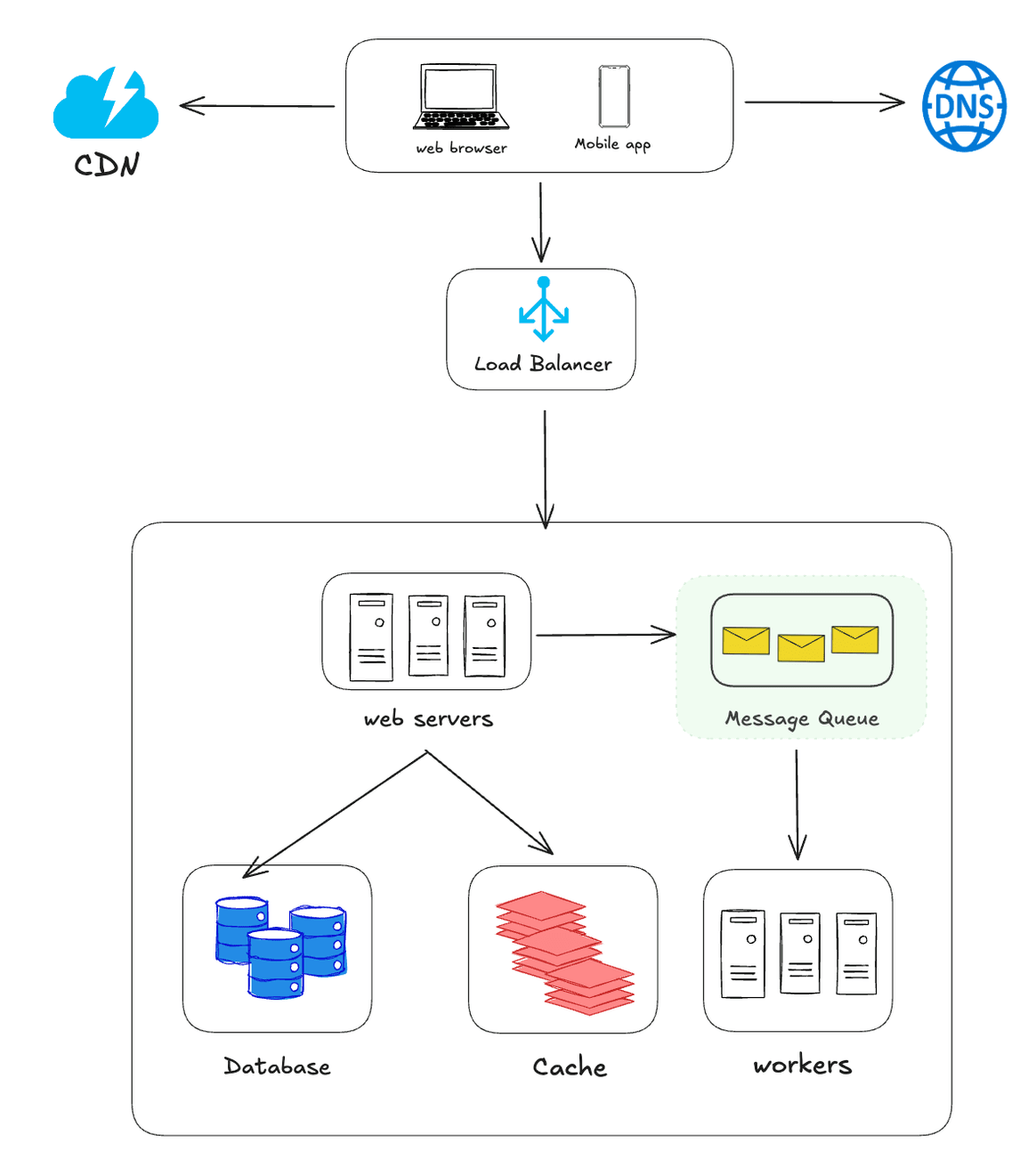
Step 6 - Message Queue
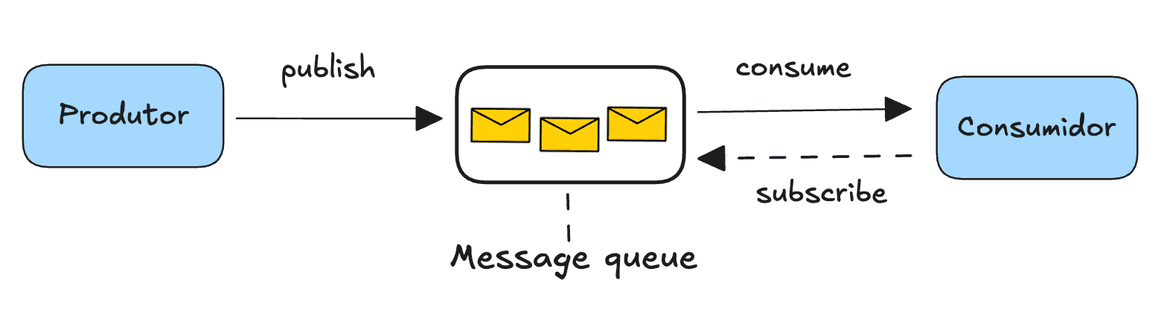
A message queue is a form of asynchronous communication between different parts of a system, allowing components to send and receive messages without being directly connected or operating at the same time.
This approach decouples message producers from consumers, improving the scalability and resilience of the system. Messages are stored in a "queue" until they can be processed by the appropriate receiver, which makes it easier to manage traffic spikes and distribute the load across multiple workers or services.
Message queues are used in distributed systems to ensure reliable delivery of information, support batch processing, and integrate different applications or software components efficiently
Step 7 - Logging, metrics, automation
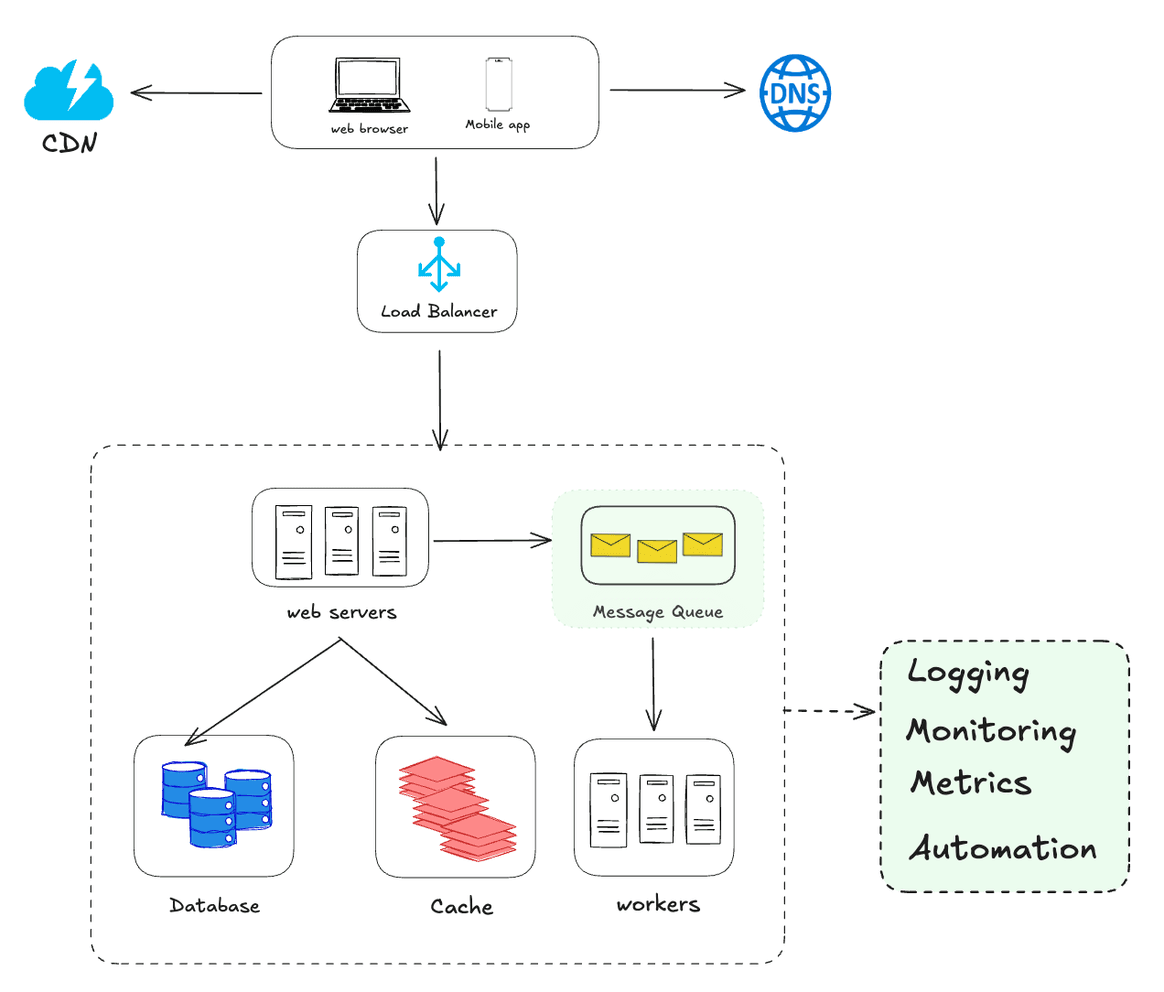
-
Logging: Monitoring error logs is important because it helps to identify errors and problems in the system. You can monitor error logs at per server level or use tools to aggregate them to a centralized service for easy search and viewing
-
Metrics: Collecting different types of metrics help us to gain business insights and understand the health status of the system. Some of the following metrics are useful:
- Host level metrics: CPU, Memory, disk I/O, etc.
- Aggregated level metrics: for example, the performance of the entire database tier, cache tier, etc.
- Key business metrics: daily active users, retention, revenue, etc.
- Automation: When a system gets big and complex, we need to build or leverage automation tools to improve productivity. Continuous integration is a good practice, in which each code check-in is verified through automation, allowing teams to detect problems early. Besides, automating your build, test, deploy process, etc. could improve developer productivity significantly
Step 8 - Data centers
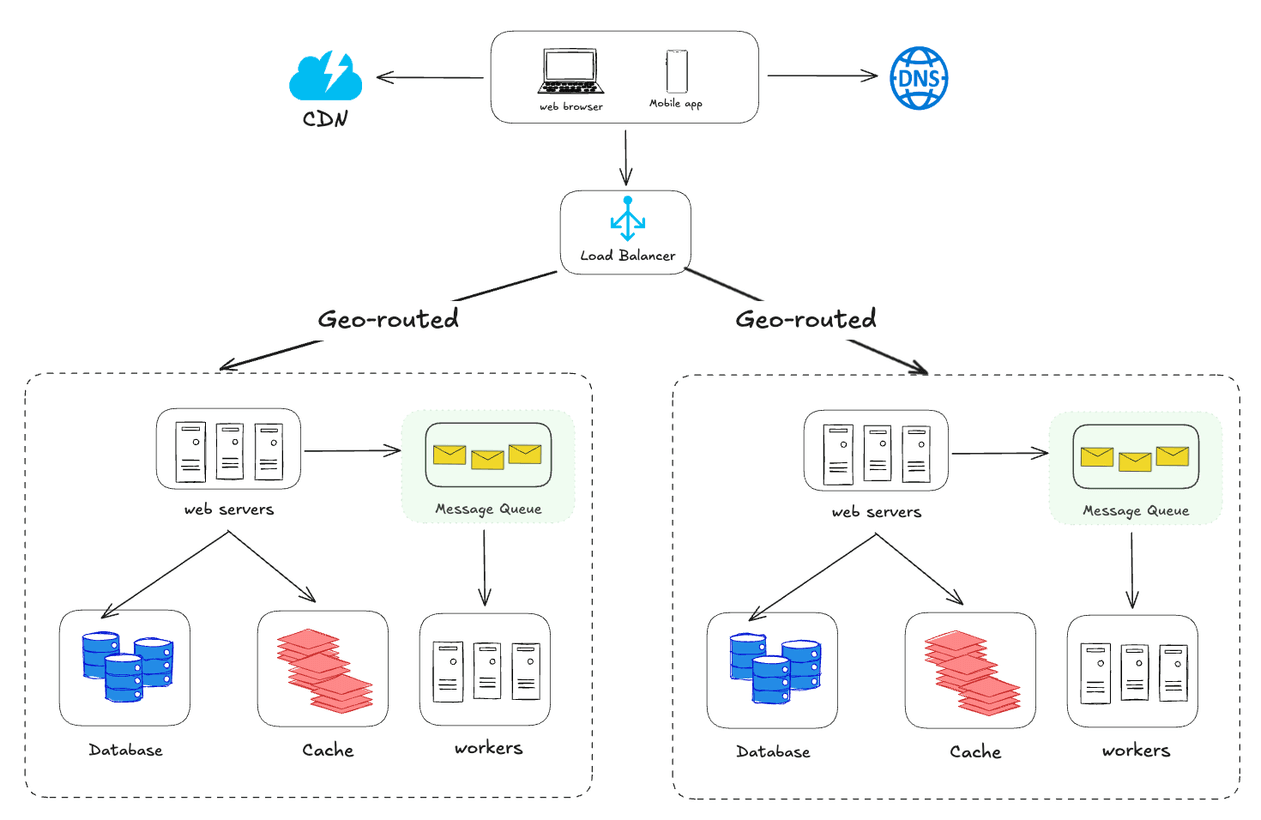
In normal operation, users are geoDNS-routed, also known as geo-routed, to the closest data center, with a split traffic of x% in US-East and (100 – x)% in US-West. geoDNS is a DNS service that allows domain names to be resolved to IP addresses based on the location of a user